Greetings to all!
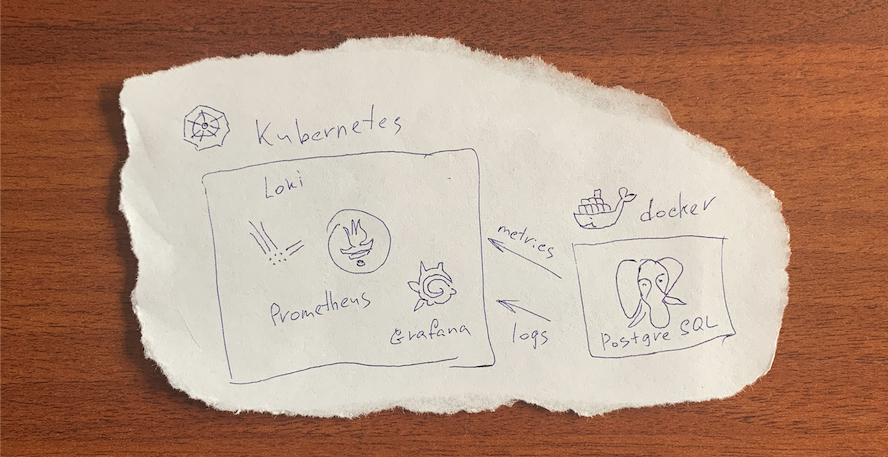
As a matter of fact I haven't found so far any generalized guide on logging and monitoring of metrics from external systems to Kubernetes on the web. Here I want to share with you my own version. First of all it is supposed that you have already got working Prometheus and other services.
As an example I use third-party data for stateful service RDBMS PostgreSQL in a Docker container. In our company we also use the Helm package manager, and you'll find how it works below. You can see same examples in this article below. You can see same examples in this article below. For a complete solution we create a nested chart.
Logging
Many companies use ELK stack for centralized logging (Elasticsearch + Logstash + kibana). In our case we don't need to index the content and I apply lightweight Loki. It is available and can be installed as a Helm package. We added it as subchart having changed values for ingress & pv.
values.yaml
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
hosts:
- host: kube-loki.example.domain
paths:
- /
tls: []
....
persistence:
type: pvc
enabled: true
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
size: 100Gi
finalizers:
- kubernetes.io/pvc-protection
existingClaim: "pv-loki"
We use Loki Docker Logging Driver for log sending to instance Loki.
You have to set it up as a Docker plugin on all hosts from which you want to get logs. There are several ways to use plugin. My choice is to put it in the yaml file of Docker Compose which is a part of Ansible playbook.
postgres.yaml
where is loki_url: kube-loki.example.domain/loki/api/v1/push
- name: Run containers
docker_compose:
project_name: main-postgres
definition:
version: '3.7'
services:
p:
image: "{{ postgres_version }}"
container_name: postgresql
restart: always
volumes:
- "{{ postgres_dir }}/data:/var/lib/postgresql/data"
- "{{ postgres_dir }}/postgres_init_scripts:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d"
environment:
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: {{ postgres_pass }}
POSTGRES_USER: {{ postgres_user }}
ports:
- "{{ postgres_ip }}:{{ postgres_port }}:5432"
logging:
driver: "loki"
options:
loki-url: "{{ loki_url }}"
loki-batch-size: "{{ loki_batch_size }}"
loki-retries: "{{ loki_retries }}"
...
where is loki_url: kube-loki.example.domain/loki/api/v1/push
Metrics
PostgreSQL metrics are collected to Prometheus with a postgres_exporter. See extension of Ansible playbook file below.
postgres.yaml
...
pexp:
image: "wrouesnel/postgres_exporter"
container_name: pexporter
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
DATA_SOURCE_NAME: "postgresql://{{ postgres_user }}:{{ postgres_pass }}@p:5432/postgres?sslmode=disable"
ports:
- "{{ postgres_ip }}:{{ postgres_exporter_port }}:9187"
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "5m"
...
For better clarity the names of external stateful services are presented with Endpoints.
postgres-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
name: postgres-exporter
subsets:
- addresses:
- ip: {{ .Values.service.postgres.ip }}
ports:
- port: {{ .Values.service.postgres.port }}
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: postgres-exporter
labels:
chart: "{{ .Chart.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Version | replace "+" "_" }}"
spec:
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: {{ .Values.service.postgres.port }}
targetPort: {{ .Values.service.postgres.port }}
Prometheus settings for getting data from postgres_exporter are tuned by means of value editing in the subchart.
values.yaml
scrape_configs:
...
- job_name: postgres-exporter
static_configs:
- targets:
- postgres-exporter.applicationnamespace.svc.cluster.local:9187
labels:
alias: postgres
...
For visualisation of data install a proper dashboard for Grafana and add datasource. That can be done with values of Grafana subchart. See how it looks below.
How it looks


I hope my first brief article in English will help you to understand basic ideas of this solution and save your time when adjusting monitoring and logging procedures of external services in Loki/Prometheus in Kubernetes.